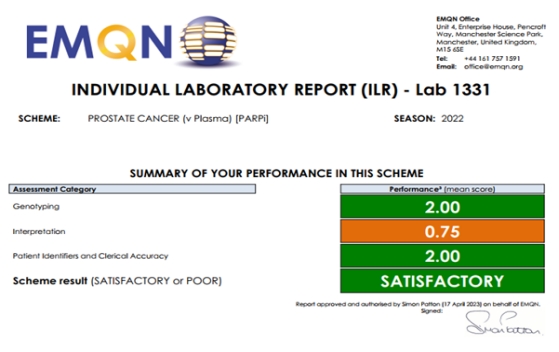
On May 15, Department of Pathology of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University passed 2022 External Quality Assessment (EQA) of European Molecular Genetics Quality Network (EMQN), involving five next-generation sequencing (NGS) schemes, and was awarded the certificate of competency. The five schemes include non-small cell lung cancer (plasma/ctDNA), non-small cell lung cancer (tissue), ovarian cancer/prostate cancer (somatic), ovarian cancer/breast cancer/prostate cancer/pancreatic cancer (germline), and prostate cancer (plasma/ctDNA). The Department of Pathology of the Second Xiangya Hospital is the only public hospital in China that has been awarded the certificate of competency in terms of the prostate cancer (plasma/ctDNA) scheme, which aims to assess the ability of laboratories globally to detect the HRR gene variation of prostate cancer based on liquid biopsy technology, including the experimental process, bioinformatics analysis, and report interpretation, etc. The other four are third-party testing institutes. This indicates that the liquid tumor biopsy (ctDNA) technology of Second Xiangya Hospital has reached a leading position in China.
Solid tumor MRD (small residual lesion) detection provides systematic detection of ctDNA in tumor plasma for patients undergone surgery and neoadjuvant chemotherapy, enabling extensive applications, and is also the latest area of development of NGS detection technology. The MRD technology based on NGS detection of pathological tissue is also the most authoritative and widely adopted. The Department of Pathology not only closely follows the forefront of technology and application development, but also develops ctDNA detection technology and quality control system, providing qualified services for a great number of patients.
Recently, the Department of Pathology also passed 2023 NCCL EQA with full marks, involving several projects: EGFR, KRAS, and BRAF gene mutation detection (PCR), FISH detection of HER2 amplification in breast cancer, and EML4-ALK fusion gene detection (FISH). The high-quality molecular detection quality control system and detection level of the Department of Pathology were fully demonstrated by the continuous success in passing EQA from authoritative institutions at home and abroad. The Department of Pathology will continuously adhere to the principle of "quality first" and make efforts to provide patients with reliable and accurate molecular detection services, as a result to facilitate accurate diagnosis and treatment.
EMQN was founded in 1998, headquartered in Manchester, the UK, is an international non-profit institute providing professional EQA for diagnostic clinical genomic testing. It is accredited by the United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) and the Accreditation Criteria for Proficiency Testing Providers (ISO17043), and its EQA is among the highest standards of accreditation for clinical laboratories in molecular genetics in the world.